RS485 is a differential signal transmission standard widely used in industrial control, automation systems, and communication networks. With its advantages of long-distance transmission and strong anti-interference capabilities, RS485 has found extensive application in complex environments. However, in practical usage, RS485 chips face multiple potential electrical threats such as Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), Electrical Fast Transients (EFT), Surge, and common-mode interference. Therefore, designing effective protection mechanisms is essential to ensure the reliability and stability of RS485 systems.
Main Threats to RS485 Chips
1. Electrostatic Discharge (ESD): ESD is caused by the sudden release of static electricity accumulated on the human body or equipment. The resulting high instantaneous voltage and current can damage the I/O or power pins of the chip.
2. Electrical Fast Transients (EFT): EFTs are fast transient voltage pulses caused by switching operations or relay movements. They may interfere with or damage RS485 communications.
3. Surge: Typically caused by lightning strikes or power switching, surges are high-energy transient overvoltages. The associated high transient currents may permanently damage the chip.
4. Common-Mode Interference: Since RS485 uses differential signaling, common-mode interference can impact signal integrity and result in communication errors.
Taking air conditioners as an example, their application environments are diverse and complex. Air conditioning systems can be categorized into commercial and residential types, or by function into multi-split and single-split units. Regardless of the type, air conditioners often operate in challenging environments—such as central HVAC systems in buildings—with complex and high-voltage power systems, and exposure to extreme weather conditions like high humidity, dryness, and thunderstorms. These conditions pose significant electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) challenges for the systems.
Protection Mechanisms in RS485 Chips
To address the threats mentioned above, Amazing Microelectronic Corp. has enhanced both EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) immunity and EMS (Electromagnetic Susceptibility) tolerance in the design of its RS485 chips. Below are the measured protection capabilities of the
1. ESD (IEC61000-4-2)
Even without additional TVS protection, the AZRS5054PA can withstand up to 15kV of ESD on the bus pins while remaining fully functional. (See Figure 1: Test Setup)

Figure 1: Test Setup
Tested at 5kV/100kHz for 60s, the AZRS5054PA can pass 4kV Class B tests. (See Figure 2: EFT Test Setup and Waveform) The chip successfully receives and recovers transmitted data.


Figure 2: EFT Test Setup and Waveform
3. Common-Mode Interference
Thanks to its unique internal design, the AZRS5054PA effectively suppresses common-mode interference and improves the robustness of differential signal transmission. While the EIA/TIA-485 standard requires tolerance from -7V to +12V, the AZRS5054PA withstands ±20V common-mode disturbance and still transmits signals reliably. (See Figure 3: Signal Waveform)
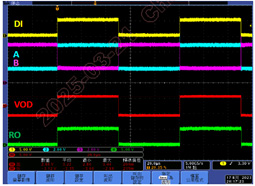
Figure 3: Signal Waveform
4. Surge (IEC61000-4-5)
Using a standard EOS test setup, the AZRS5054PA bus pins endure ±65V surge energy under an 8/20us 2-ohm condition without TVS protection, without any functional damage. (See Figure 4: Surge Test Environment)

Figure 4: Surge Test Environment
System-Level TVS Protection Matching
In addition to the chip's own high EMC capabilities, Amazing Microelectronic Corp. also recommends pairing it with the AZ4212-01G TVS diode for enhanced system-level protection. As shown in Figure 5, the AZ4212-01G offers surge tolerance up to 25A and ESD clamping voltage as low as 17V at 8kV. The combination of AZRS5054PA with AZ4212-01G creates a safer and more reliable RS485 protection solution.

Figure 5: TVS Specifications and Interface Circuit Diagram
A well-designed RS485 protection mechanism is the key to ensuring its reliable operation in complex environments. Through the integration of ESD protection, EFT and surge defenses, suppression of common-mode interference, power protection, and optimized PCB layout, the anti-interference capability and system reliability can be significantly improved. In actual applications, the choice of a suitable TVS protection solution should be based on the specific environment and requirements to guarantee long-term system stability. With these comprehensive measures in place, RS485 chips can maintain stable performance even under the harsh electrical conditions typically found in air conditioning systems, ensuring communication reliability and safety.
